When you update the Deployment with a RollingUpdate strategy, Kubernetes creates a new ReplicaSet resource, and it simultaneously spins up the required number of pods on the new ReplicaSet resource while slowly spinning down the old ReplicaSet resource, as evident from the following diagram:
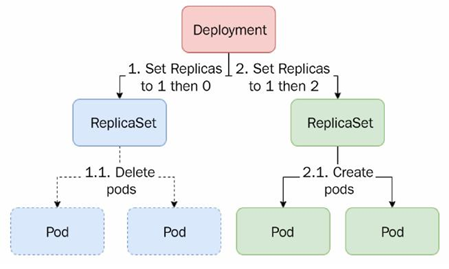
Figure 6.3 – RollingUpdate strategy
RollingUpdate is the default deployment strategy. You can use the RollingUpdate strategy in most applications, apart from ones that cannot tolerate more than one version of the application at a given time.
Let’s update the nginx Deployment resource using the RollingUpdate strategy. We will reuse the standard nginx-deployment.yaml file that we used before. Use the following command and see what happens to the ReplicaSet resources:
$ kubectl apply -f nginx-deployment.yaml && kubectl get replicaset -w deployment.apps/nginx configured
| NAME | DESIRED | CURRENT | READY | AGE |
| nginx-6799fc88d8 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 49s |
| nginx-6889dfccd5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4s |
| nginx-6799fc88d8 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 53s |
| nginx-6889dfccd5 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 8s |
| nginx-6799fc88d8 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 57s |
| nginx-6889dfccd5 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 11s |
| nginx-6799fc88d8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 60s |
As we see, the old ReplicaSet resource—nginx-6799fc88d8—is being rolled down, and the new ReplicaSet resource—nginx-6889dfccd5—is being rolled out simultaneously.
The RollingUpdate strategy also has two options—maxUnavailable and maxSurge.
While maxSurge defines the maximum number of additional pods we can have at a given time, maxUnavailable defines the maximum number of unavailable pods we can have at a given time.
Tip
Set maxSurge to 0 if your application cannot tolerate more than a certain number of replicas. Set maxUnavailable to 0 if you want to maintain reliability and your application can tolerate more than the set replicas. You cannot specify 0 for both parameters, as that will make any rollout attempts impossible. While setting maxSurge, ensure your cluster has spare capacity to spin up additional pods, or the rollout will fail.
Using these settings, we can create different kinds of custom rollout strategies—some popular ones are discussed in the following sections.